サーバーサイドプログラマーのためのReact.js 入門 4. react-router、更新系ページの追加
React.jsの仕事の納期におわれ1ヶ月ぶりになってしましたましたが、今回は
- react-router の導入
- 更新系ページの追加
を行い、Todoアプリを完成したいと思います。

react-router
JSで作られたアプリはSPA(Single Page Application)と呼ばれているように物理的には1つのページ(URL)内で動作します。しかしアプリがURLに対応してないとブラウザーのbackボタンに対応出来ないないですし、プログラムの構成を考えるのも面倒です。
そこで、URLとアプリ(JS)を対応づける react-router を使うと Rails の routes のように URLにアプリを対応づけ出来、今ままで Rails 等で開発してきた人にはとても嬉しいことです。
react-router には チュートリアル や充実したドキュメント がありますので、しっかり理解するには チュートリアル を試し、ドキュメント に目を通しておくと良いと思います。
react-router を組み込んでみる
前回作った TODO 一覧に react-router を組み込んで Railsのshow ページと同じものを追加してみましょう。

react-router インストール
$ cd frontend $ npm install --save react-router
index.js ページの作成
前回作ったアプリは全てのコードが src/js/index.js にありましたが、 一覧の機能は src/js/IndexPage.js にしましょう。 src/js/index.js をコピーまたはリネームし src/js/IndexPage.js を作ります(修正は次で行います)
src/js/index.js はルーテイング情報を書きます。
import React from 'react'
import { render } from 'react-dom'
import { Router, Route, IndexRoute, hashHistory } from 'react-router'
import IndexPage from './IndexPage'
import ShowPage from './ShowPage'
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" >
<IndexRoute component={IndexPage}/>
<Route path="/:id" component={ShowPage}/>
</Route>
</Router>
),
document.getElementById("example")
)
ページ繊維の履歴管理にはいくつかの方法が選べます。 ドキュメントのHistories に説明があります。
今回はhashHistoryを使ってみます、ドキュメントに本来は browserHistory を使うべきだと書かれていますが browserHistory を使うと Rails で使っているURLがかぶってしまうので、ここでは /#URL を使うhashHistoryにしました Router history= で hashHistory を指定しています。
ルーテイング は / で一覧(IndexPage.js) /ID番号 で詳細表示(ShowPage.js) が動作するように指定しています。 Rails のルーテイング同様に /:id の id の部分はパラメーターとして取得できます。
画面へReact.jsの結果を表示する render() はこちらに移動します。
IndexPage.js 変更
前回の index.js をコピーした IndexPage.js は少し変更します。変更点はコメントに ★ を付けたところで
- import の変更、
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'は削除されました - IndexPageクラスが外部から参照できるように export default を追加
- Showpage.js へのリンク
<Link>は<a>タグが作成されます、Railsのlink_toと同じようなものですね。<Link>は単純に<a>を生成しているのでは無く色々な処理を行っています - 画面へReact.jsの結果を表示する render() は index.js に移行したので削除されました
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router' // ★
import axios from 'axios'
export default class IndexPage extends Component { // ★
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todos: []}
}
componentDidMount() {
axios.get('/todos.json').then((response) => {
this.setState({todos: response.data})
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<h2>List of Todos</h2>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}/>
</div>
)
}
}
class TodoList extends Component {
render() {
return(
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Due</th>
<th>Task</th>
<th colSpan="3"></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.props.todos.map((todo) => (<TodoListItem key={todo.id} todo={todo} />))}
</tbody>
</table>
)
}
}
TodoList.propTypes = {
todos: PropTypes.array.isRequired
}
class TodoListItem extends Component {
render() {
return(
<tr>
<td> {this.props.todo.due} </td>
<td> {this.props.todo.task} </td>
<td><Link to={`/${this.props.todo.id}`}>Show</Link></td> // ★
</tr>
)
}
}
TodoListItem.propTypes = {
todo: PropTypes.object.isRequired
}
ShowPage.js 作成
詳細表示のページ ShowPage.js は以下のようになります。 URLで指定される ID番号は this.props.params.id で取得できます。その他は特に説明する事はないと思います。
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router'
import axios from 'axios'
export default class ShowPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todo: {}}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.todoFind(this.props.params.id)
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
this.todoFind(nextProps.params.id)
}
todoFind(todoId) {
axios.get(`/todos/${todoId}.json`).then((response) => {
this.setState({todo: response.data})
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<h2>Show</h2>
<p>
<strong>Due:</strong>
{this.state.todo.due}
</p>
<p>
<strong>Task:</strong>
{this.state.todo.task}
</p>
<Link to="/">Back</Link>
</div>
)
}
}
ShowPage.propTypes = {
params: PropTypes.object
}
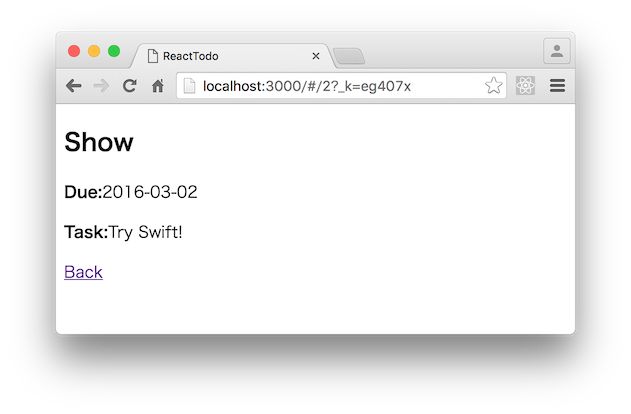
ここまで出来れば、上の画像のように 一覧の show リンクをクリックすると詳細画面が表示されます
更新系ページの追加
Rails の CSRF対策を無効にする
追加・更新を行うにはRuby on RailsのCSRF対策に対応しないといけませんが、今回は安易にスキップします。 実際のアプリでは行わないで下さいね!
- ../app/controllers/todos_controller.rb
class TodosController < ApplicationController before_action :set_todo, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy] skip_before_action :verify_authenticity_token # ★
新規作成ページのルーティング情報を追加
まずは、index.js にルーティング情報を追加します、コメントに ★ を付けたところ
import { render } from 'react-dom'
import { Router, Route, IndexRoute, hashHistory } from 'react-router'
import IndexPage from './IndexPage'
import ShowPage from './ShowPage'
import NewPage from './NewPage' // ★
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" >
<IndexRoute component={IndexPage}/>
<Route path="/new" component={NewPage}/> // ★
<Route path="/:id" component={ShowPage}/>
</Route>
</Router>
),
document.getElementById("example")
)
新規作成ページの追加
新規作成ページに対応する NewPage、 TODO情報のフォームに対応する TodoForm に分けました。Railsと同じように編集ページと共通になるフォーム部分を別のコンポーネント(モジュール)にしました。
React.js では state(状態、データ)は上位のコンポーネントに置き、下位のコンポーネントへpropsで渡します。 またボタンを押した等のイベントは下位のコンポーネントでは処理せずに上位のコンポーネントで処理するのが定跡(ベストプラクティス)です。
TODO情報をバックエンドに登録(ポスト)する todoCreateメソッド はNewPageに置いています。 todoCreateメソッド は下位のTodoFormの中にも置けますが、登録した後に state が変化する事は良くあるので、この方が良いと思います。また、通信やモデル(ここでは stateのtodo)変更は上位のコンポーネントに集めるのは下位コンポーネントの汎用性やコードの見通しがよくなります。
todoCreateメソッド内の this.props.history.push() は指定されたURL(Path)への遷移を起こします。
formChangeメソッドに付いては TodoForm の方で説明します。
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router'
import axios from 'axios'
import TodoForm from './TodoForm'
export default class NewPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todo: {}}
}
todoCreate() {
axios.post('/todos.json',
{todo: this.state.todo}).then((response) => {
this.props.history.push(`/${response.data.id}`)
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
formChange(todo) {
this.setState({todo: todo})
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<h2>New</h2>
<TodoForm todo={this.state.todo} buttonLable="Create" onChange={this.formChange.bind(this)} onSubmit={this.todoCreate.bind(this)} />
<Link to="/">Back</Link>
</div>
)
}
}
NewPage.propTypes = {
params: PropTypes.object,
history: PropTypes.object
}
TodoForm は主にを <form> フォームを扱っています。 React.js でのフォームの扱いは ドキュメントのForms に書かれているます。フォーム内の <input> のハンドリングは、全ての変更をアプリのコードで扱う Controlled Components と Reactに任せる
Uncontrolled Components があります。ここでは分かりやすい Controlled Components を使っています。
Controlled Componentsでは<input> に変化がおきるとその変化をアプリのコードで state に反映し、stateの値から <input> を再表示します(再表示は React.js が行います)。
ここでは state は上位コンポーネントにあるので、上位コンポーネントの formChange メソッドを呼び出しています。その結果、上位コンポーネントから変更された state の値を props で受け取った TodoForm が再表示されます(再表示は React.js が行います)。
React.js では <input> の値などを参照するには タグに ref 属性を指定し、コードからは this.refs.ref属性値 で取得します。 refに付いては ドキュメントのRefs to Components に書かれています。
submitボタンが押された時の動作はここでは <button> の onClick でハンドリングしています。 event.preventDefault() で他のタグへのイベントの伝搬をキャンセルし、上位コンポーネントのメソッドを呼び出しています。
日付の入力はRailsでは年月日の <select> になりますが、面倒なので通常の <input type="text"> にしました。たぶんカレンダー入力の React Date Picker などを使えば良いのかなと思います。
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
export default class TodoForm extends Component {
change() {
this.props.onChange({due: this.refs.due.value, task: this.refs.task.value})
}
submit(event) {
event.preventDefault()
this.props.onSubmit()
}
render() {
return(
<form>
<div className="field">
<label htmlFor="todo_due">Due</label><br/>
<input type="text" ref="due" id="todo_due" value={this.props.todo.due} onChange={this.change.bind(this)} />
</div>
<div className="field">
<label htmlFor="todo_task">Task</label><br/>
<input type="text" ref="task" id="todo_task" value={this.props.todo.task} onChange={this.change.bind(this)} />
</div>
<div className="actions">
<button onClick={this.submit.bind(this)}>{this.props.buttonLable}</button>
</div>
</form>
)
}
}
TodoForm.propTypes = {
todo: PropTypes.object.isRequired,
buttonLable: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
onChange: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
onSubmit: PropTypes.func.isRequired
}
IndexPage.js の変更1
新規作成へのリンクを追加します
*** import は変更なし ***
export default class IndexPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todos: []}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.todoAll()
}
componentWillReceiveProps() {
this.todoAll()
}
todoAll() {
axios.get('/todos.json').then((response) => {
this.setState({todos: response.data})
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
todoDelete(todoId) {
axios.delete(`/todos/${todoId}.json`).then(() => {
this.todoAll()
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<h2>List of Todos</h2>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}/>
<br />
<Link to="/new">New Todo</Link> // ★
</div>
)
}
}
*** 以下は同じ ***
IndexPage.js の変更2
新規作成機能を追加し試してみると、新規追加したデータが表示されない時があります。前回書いたように
- 一度表示されたコンポーネントはインスタンスがメモリ上に残っているので、他のコンポーネントから再表示を起こしても componentDidMount は実行されません。その時は componentWillReceiveProps が呼び出されます。
一覧の再表示が正しく行われるように componentWillReceivePropsメソッドでもデータを取得するように変更します。
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router'
import axios from 'axios'
export default class IndexPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todos: []}
}
componentDidMount() { // ★
this.todoAll()
}
componentWillReceiveProps() { // ★
this.todoAll()
}
todoAll() { // ★
axios.get('/todos.json').then((response) => {
this.setState({todos: response.data})
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
todoDelete(todoId) {
axios.delete(`/todos/${todoId}.json`).then(() => {
this.todoAll()
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
render() {
*** 以下は同じ ***
変更ページの追加
新規作成ページと同様なので特に説明する必要はないと思います
- index.js
import React from 'react'
import { render } from 'react-dom'
import { Router, Route, IndexRoute, hashHistory } from 'react-router'
import IndexPage from './IndexPage'
import ShowPage from './ShowPage'
import EditPage from './EditPage' // ★
import NewPage from './NewPage'
render((
<Router history={hashHistory}>
<Route path="/" >
<IndexRoute component={IndexPage}/>
<Route path="/new" component={NewPage}/>
<Route path="/:id" component={ShowPage}/>
<Route path="/:id/edit" component={EditPage}/> // ★
</Route>
</Router>
),
document.getElementById("example")
)
- EditPage.js
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router'
import axios from 'axios'
import TodoForm from './TodoForm'
export default class EditPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todo: {}}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.todoFind(this.props.params.id)
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
this.todoFind(nextProps.params.id)
}
todoFind(todoId) {
axios.get(`/todos/${todoId}.json`).then((response) => {
this.setState({todo: response.data})
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
todoUpdate() {
axios.put(`/todos/${this.props.params.id}.json`,
{todo: this.state.todo}).then((response) => {
this.props.history.push(`/${response.data.id}`)
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
formChange(todo) {
this.setState({todo: todo})
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<h2>Edit</h2>
<TodoForm todo={this.state.todo} buttonLable="Update" onChange={this.formChange.bind(this)} onSubmit={this.todoUpdate.bind(this)} />
<Link to={`/${this.state.todo.id}`}>Show</Link> |
<Link to="/">Back</Link>
</div>
)
}
}
EditPage.propTypes = {
params: PropTypes.object,
history: PropTypes.object
}
- IndexPage.js
*** 上部は同じ ***
class TodoListItem extends Component {
render() {
return(
<tr>
<td><Link to={`/${this.props.todo.id}`}>Show</Link></td>
<td><Link to={`/${this.props.todo.id}/edit`}>Edit</Link></td> // ★
</tr>
)
}
}
TodoListItem.propTypes = {
todo: PropTypes.object.isRequired
}
*** 以下は同じ ***
削除機能の追加
TodoListItemに 削除用リンクを追加し、クリックした際にバックエンドの削除APIを呼び出す todoDelete メソッドを IndexPageコンポーネントに追加しました。
削除確認のダイアログをどのコンポーネントで出すかは考慮の余地があると思います。今回は確認ダイアログはUIの一部と考え、下位コンポーネントで確認は行うようにしました。 上位コンポーネントで出すという考え方もあると思います。
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react'
import { Link } from 'react-router'
import axios from 'axios'
export default class IndexPage extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {todos: []}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.todoAll()
}
componentWillReceiveProps() {
this.todoAll()
}
todoAll() {
axios.get('/todos.json').then((response) => {
this.setState({todos: response.data})
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
todoDelete(todoId) { // ★
axios.delete(`/todos/${todoId}.json`).then(() => {
this.todoAll()
}).catch((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
render() {
return(
<div>
<h2>List of Todos</h2>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos} onDelete={this.todoDelete.bind(this)} />
</div>
)
}
}
class TodoList extends Component {
render() {
return(
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Due</th>
<th>Task</th>
<th colSpan="3"></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.props.todos.map((todo) => (<TodoListItem key={todo.id} todo={todo} onDelete={this.props.onDelete} />))} // ★
</tbody>
</table>
)
}
}
TodoList.propTypes = {
todos: PropTypes.array.isRequired,
onDelete: PropTypes.func.isRequired // ★
}
class TodoListItem extends Component {
destroy(event) { // ★
event.preventDefault()
if (confirm("Are you sure ?")) {
this.props.onDelete(this.props.todo.id)
}
}
render() {
return(
<tr>
<td> {this.props.todo.due} </td>
<td> {this.props.todo.task} </td>
<td><Link to={`/${this.props.todo.id}`}>Show</Link></td>
<td><Link to={`/${this.props.todo.id}/edit`}>Edit</Link></td>
<td><Link to='' onClick={this.destroy.bind(this)}>Destroy</Link></td> // ★
</tr>
)
}
}
TodoListItem.propTypes = {
todo: PropTypes.object.isRequired,
onDelete: PropTypes.func.isRequired // ★
}
まとめ
今回までの知識で React.js でアプリ作成は出来るようになるとおもいます。 React.js以外のライブラリーを組みわせるには、もう少し知識がいりますが大抵のことは ドキュメント に書かれていますし、検索をすると Stackoverflow に答えがみつかると思います。
今回、仕事で1万行以上の React.js を書きましたが、Reactの考え方(設計思想)になれるまでは時間がかかりますが、なれれば動きの分かり易いコードが出来る良いライブラリーだと思います。